NMAP has tons of scripts to do things like DoSing targets or exploiting them.
-
Script scanning is normally done in combination with a port scan, because scripts may be run or not run depending on the port states found by the scan.
-
By default, Nmap does host discovery and then performs a port scan.
-
With the '-sn' (No port scan) option it is possible to run a script scan without a port scan and only host discovery. In this case only host scripts will be eligible to run.
-
In previous releases of Nmap, -sn was known as -sP (ping scan).
There are four types of NSE scripts:
- Prerule scripts – scripts that run before any of Nmap’s scan operations, they are executed when Nmap hasn’t gathered any information about a target.
- Host scripts – scripts executed after Nmap has performed normal operations such as host discovery, port scanning, version detection, and OS detection against a target host.
- Service scripts – scripts run against specific services listening on a target host
- Postrule scripts – scripts run after Nmap has scanned all of its target hosts.
These scripts are futher grouped under following categories:
-
Auth: Use to test whether you can bypass authentication mechanism
-
Broadcast: Use to find other hosts on the network and automatically add them to scanning que.
-
Brute: Use for brute password guessing.
-
Discovery: Use to discover more about the network.
-
Dos (Denial of Service): Use to test whether a target is vulnerable to DoS
- DOS is an attack used to deny legitimate users access to a resource such as accessing a website, network, emails, etc. or making it extremely slow. It is usually implemented by hitting the target resource such as a web server with too many requests at the same time.
-
Exploit: Use to actively exploit a vulnerability
-
Fuzzer: Use to test how server responds to unexpected or randomized fields in packets and determine other potential vulnerabilities
-
Intrusive: Use to perform more intense scans that pose a much higher risk of being detected by admins.
-
Malware: Use to test target for presence of malware
-
Safe: Use to perform general network security scan that's less likely to alarm remote administrators
-
Vuln: Use to find known vulnerabilities on the target
-
default: These include scripts whic are fast and excludes brute force authentication crackers, web spiders, and any other scripts which can take minutes or hours to scan a single service and less privacy invasive (means do not use external services like whois lookup).
These scripts are almost always in the safe category though there may be few intrusive scripts.
Run them using -sC or -A or --script=default option.
A few default scripts are:
- identd-owners (determines the username running remote services using identd)
- http-auth (obtains authentication scheme and realm of web sites requiring authentication)
- ftp-anon (tests whether an FTP server allows anonymous access)
-
version: These scripts are an extension to the version detection feature and cannot be selected explicitly. They are selected to run only if version detection (-sV) was requested.They do not produce service or host script results.
-
external: These scripts may send data to a third-party database or other network resource.Example: whois-ip, which makes a connection to whois servers to learn about the address of the target.Most scripts involve traffic strictly between the scanning computer and the client; any that do not are placed in this category.Third-party database will record anything you send to them, which in many cases will include your IP address and the address of the target.
--script-updatedb
This option updates the script database found in 'scripts/script.db' which is used by Nmap. It is only necessary to update the database if you have added or removed NSE scripts from the default scripts directory or if you have changed the categories of any script.
nmap --script-updatedb
- Some other Nmap options have effects on script scans.Example a version scan (-sV) automatically executes the scripts in the version category.
Using * Wildcard
This is useful when you want to select scripts with a given name pattern.
Example: To run all scripts with name starting with ssh, run the command:
nmap --script "ssh-*" [TARGET]
Syntax
nmap --script [SCRIPPT CATEGORY or NAME] [TARGET] [OPTIONS]
- Options like -d (debug) or -v (verbose) are optional
Scripts in Action
Finding vulnerabilities on a target
nmap --script vuln [TARGET]
If vulnerability found nmap's output will list it's findings along with applicable CVEs and links to any exploits that exist in exploit-DB.
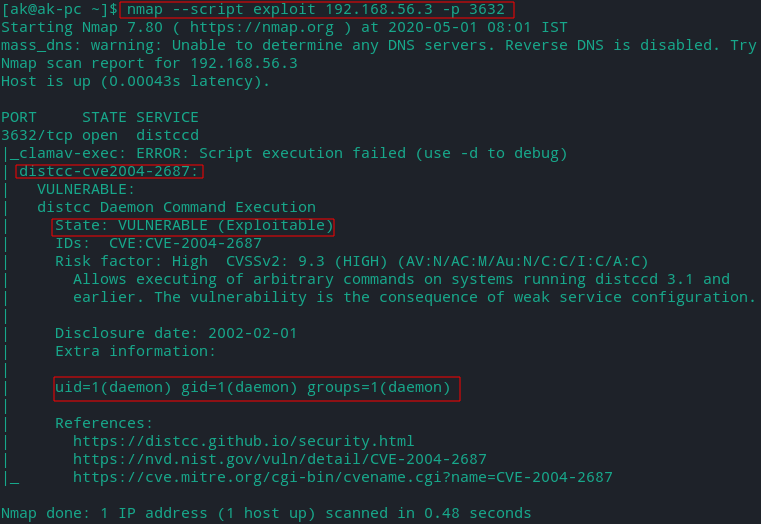
Actively Exploit Detected Vulnerabilities
nmap --script exploit [TARGET]
Brute Force Passwords
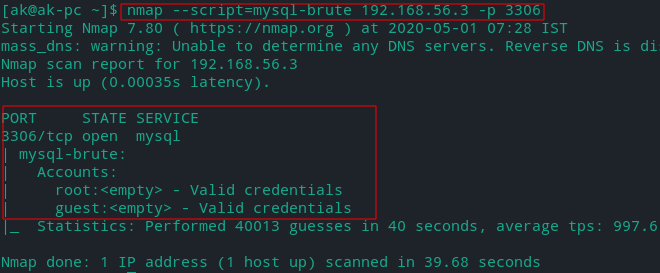
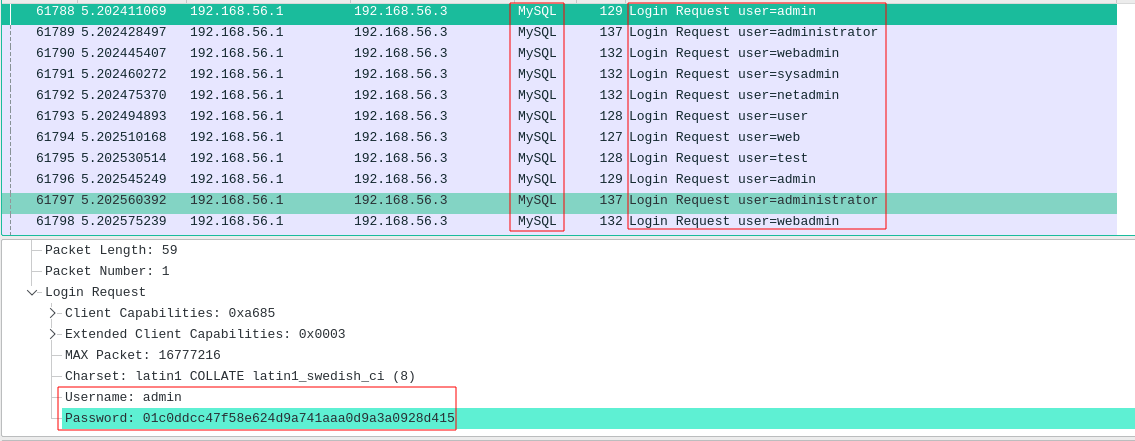
Nmap contains scripts for brute forcing dozens of protocols, including http-brute, oracle-brute, snmp-brute, etc. Use the following command to perform brute force attacks to guess authentication credentials of a remote server.
nmap --script brute [TARGET]
Check whether the target is vulnerable to DoS
nmap --script dos [TARGET]
This will tell you whether the target is vulnerable without actually launching a dos attack.
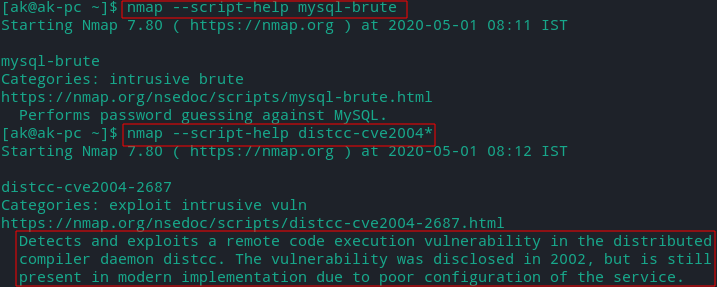
Get help regarding a script
sudo nmap --script-help [script name].nse
Search for scripts
Use Google
OR
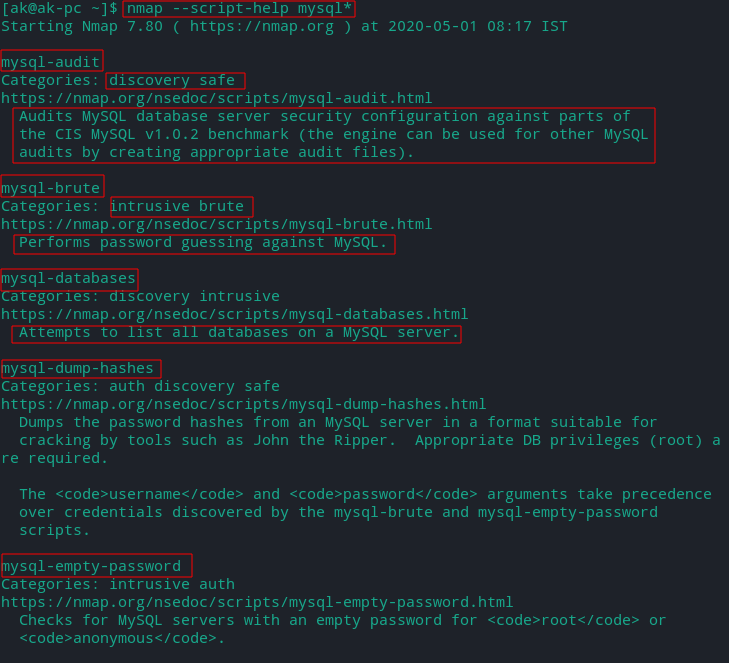
--script help * (service or protocol name)*
Using Boolean Expressions (or,and,not)
Select scripts using boolean expressions which can be build using the and, or, and not operators. And names in a Boolean expression may be a category, a filename from script.db, or all.
Load scripts from the default or broadcast categories
nmap --script "default or broadcast" [TARGET]
OR
nmap --script default,broadcast [TARGET]
Load all scripts omitting those in the vuln category
nmap --script "not vuln" [TARGET]
Load scripts in the default, or broadcast categories, leaving out those with names starting with ssh-
nmap --script "(default or broadcast) and not ssh-*" [TARGET]
Combine categories, script names, a directory containing custom scripts or a boolean expression to load scripts
nmap --script broadcast,vuln,ssh-auth-methods,/path/to/custom/scripts [TARGET]